What is hyperconverged infrastructure? Guide to HCI
Hyperconverged infrastructure is a software-centric architecture that tightly integrates compute, storage and virtualization resources into a single, highly integrated system that usually consists of x86 hardware, along with a comprehensive software stack that includes operating systems, virtualization platforms and software management tools.
Modern businesses rely on the data center to provide the computing, storage, networking and management resources that are necessary to host vital enterprise workloads and data. But data centers can be notoriously complex places where a multitude of vendors compete to deliver myriad different devices, systems, services and software. This heterogeneous mix often struggles to interoperate -- and rarely delivers peak performance for the business without careful, time-consuming optimizations. Today, IT teams simply don't have the time to wrestle with the deployment, integration and data center management challenges posed by traditional heterogeneous environments.
The notion of convergence originally arose as a means of addressing the challenges of heterogeneity. Early on, a single vendor would gather the systems and software of different vendors into a single preconfigured and optimized set of equipment and tools that was sold as a package. This was known as converged infrastructure, or CI. Later, convergence vendors took the next step to design and produce their own line of prepackaged and highly integrated compute, storage and network gear for the data center. It was an evolutionary step now called hyperconverged infrastructure, or HCI.
Converged and hyperconverged systems are possible through a combination of virtualization technology and unified management. Virtualization enables compute, storage and networking resources to be treated as pooled resources that can be centrally provisioned and managed. Unified management lets all those resources be discovered, organized into pools, divided into performance tiers and then seamlessly provisioned to workloads regardless of where those resources are physically located. Unified management offers a quantum leap over traditional heterogeneous data center environments that might rely on multiple disparate management tools, which often didn't discover or manage all resources.
Today, the combination of virtualized hardware and associated management tooling is often treated as a standalone appliance that can operate as a single, complete hyperconverged system in the data center, or be combined with other HCI appliances to quickly and easily scale up a hyperconverged infrastructure deployment.
Let's take a closer look at hyperconverged infrastructure technology, consider its use cases and implementation, evaluate its tradeoffs, examine some current vendors and product offerings and look ahead to the future of the technology.
How does hyperconverged infrastructure work?
Too often, eclectic mixes of hardware from varied vendors have been tied together with inadequate networking gear and prove impossible to provision and manage through a single tool. The result is almost always a hodgepodge of diverse gear and software that results in confusion, oversights, security vulnerabilities, needless firefighting and wasted time on the part of IT administrators.
Hyperconverged infrastructure is founded on the two essential premises of integration and management, which arose as a means of solving two of the most perplexing problems of traditional heterogeneous data centers: suboptimal performance and fractured -- problematic -- systems management. The goal of HCI is to deliver virtualized and scalable compute, storage and network resources that are all discoverable and managed through a single pane of glass.
Beyond that basic premise, however, there are numerous variations and options available for hyperconverged infrastructure. It's important to understand the most common considerations found in HCI technology.
Hardware or software deployment
Hyperconverged infrastructure can be implemented through hardware or software:
- Hardware deployment. HCI technology arose as a hardware platform that puts compute, storage -- and sometimes network -- resources into a dedicated device often referred to as an appliance. Hardware-based HCI enables high levels of integration and optimization, which can vastly enhance key performance in vital areas, such as storage-to-CPU data transfers. Hardware HCI can be ideal when high performance is important for workloads, such as real-time data analytics tasks, and when hardware modularity and scalability are important for the business. However, hardware-based HCI tends to be proprietary to the vendor, raising costs and risking some amount of vendor lock-in. For example, hardware HCI enables a business to easily add new HCI appliances as needed without concern over management software compatibility and support. Examples of hardware-based HCI include the Dell EMC VxRack System Flex and the HPE SimpliVity 380 and 2600 platforms, among others.
- Software deployment. Conceptually, an HCI system is a hardware platform with virtualization and management software running on top. Rather than purchasing the underlying hardware, HCI can also be implemented as a software layer that is intended to discover, virtualize and manage existing hardware components. The software approach lets a business gain HCI benefits without the need for extensive new hardware investments. The disadvantage here is that existing hardware devices -- including servers and storage subsystems -- won't necessarily benefit from the tight integration and optimizations found in hardware-based HCI. HCI software is available from numerous vendors, including VMware vSAN and VMware HCI software; Nutanix Acropolis, which includes the AHV virtualization platform; Microsoft's Azure Stack, the on-premises version of Azure; and even OpenStack. The software approach can also impose architectural modifications and new monitoring demands that the HCI software layer may not provide. Thus, software-based HCI can be more complicated for businesses to implement and maintain.
Integrated or disaggregated
Hyperconverged infrastructure can follow two different approaches in terms of hardware design:
- Integrated HCI. The integrated approach is more traditional, where an HCI appliance contains a balanced mix of compute resources, including processors, memory and storage. Each appliance is termed a node, and an HCI deployment can be scaled up to include numerous nodes. Integrated HCI hardware is easy to understand and offers high performance -- everything is in the same box. But resources are finite, and workloads usually don't utilize resources evenly. When a node runs short of a resource, such as CPUs, a business would need to add an entirely new node -- even though the other resources in the new node, such as the memory and storage in this example, might not yet be used or needed. This poses the potential for wasted investment.
- Disaggregated HCI. Hyperconverged infrastructure has more recently started adopting a disaggregated architecture. Rather than putting CPUs, memory and storage all together in the same box -- appliance -- the idea is to provide different resource components in different modules. Thus, a disaggregated HCI (dHCI) hardware deployment would put CPUs and memory in one compute box, and storage in a separate storage box. All the different resource modules are tied together across a network. Although it's technically possible to also separate CPUs and memory for greater disaggregation, it's better for performance to keep CPUs and memory together in the same device, as CPUs and memory are tightly coupled in a compute environment. Disaggregated approaches promise additional flexibility, enabling the business to focus HCI investments on the resources that are most beneficial to the workloads deployed. Several HCI vendors have disaggregated HCI offerings, including Dell PowerFlex, Datrium DVX, NetApp HCI and HPE Alletra.
Deployment
Hyperconverged infrastructure has been regarded as a disruptive technology; it typically displaces existing data center hardware. Anytime that HCI is being introduced to the data center, it's important to consider how that technology will be implemented or operated. There are basically three ways to add HCI to a traditional heterogeneous data center:
- Full replacement HCI deployment. The first option is a complete replacement of the traditional environment with a hyperconverged infrastructure product. In practice, this is probably the least desirable option because it poses the maximum possible displacement of hardware -- as well as the highest potential costs. Few organizations have the capital or technological need for such an undertaking. It's more likely that a new HCI deployment will be adopted for greenfield projects, such as a second -- backup, remote or edge -- data center construction or other new build, using reference architecture where equipment capital can be invested in HCI without displacing existing hardware.
- Side-by-side HCI deployment. The second, and far more palatable, approach is a side-by-side deployment where an HCI platform is deployed in the existing data center along with traditional heterogeneous infrastructure. This approach lets businesses migrate workloads to HCI over time and can be performed over the long term. Displaced hardware can be repurposed or decommissioned in smaller, more manageable portions. It is likely that HCI will run in tandem with traditional infrastructures over the long term, and the two can easily coexist. A common use for side-by-side HCI deployment is for a private or hybrid cloud project.
- Per-application HCI deployment. The third approach also brings hyperconverged infrastructure into the existing data center environment. But rather than migrate existing workloads to the new infrastructure, the HCI is intended only to support specific new applications or computing initiatives, such as a new virtual desktop infrastructure deployment or a new big data processing cluster; previous workloads are left intact on the existing infrastructure.
Features
HCI is intended to provide the compute, storage and network resources needed to run enterprise workloads -- all tied together through a single-pane-of-glass management platform. However, competitive HCI products can offer a wide range of additional capabilities that potential adopters should consider:
- Data protection. In addition to traditional primary storage, HCI systems can include a powerful policy engine to automatically assist with varied data protection tasks including backups, snapshots, disaster recovery (DR) and storage cloning.
- Elastic replication. Advanced HCI systems can support features such as data deduplication, WAN bandwidth optimization and cross-cloud data replication. These can be vital features for public and hybrid cloud use.
- Data integrity. HCI systems can include storage management, integrity and high-availability capabilities, such as RAID and other zero-data loss features to ensure that workloads and data are always intact.
- Virtualized network function support. VNF technology is based on software-defined networking and allows for advanced features, such as stretch clustering, cloud replication and advanced security. This enables networks to extend across cloud, data center and edge environments. Other networking features found in HCI systems can include network address translation, quality of service, load balancing, routing and switching. Security can be enhanced through network features such as microsegmentation, packet inspection and network encryption.
Why is hyperconvergence important?
There are two fundamental philosophies in data center infrastructure selection: homogeneity, meaning one or same; and heterogeneity, meaning many or different. A homogeneous data center uses equipment -- and often software and services -- from a single IT vendor. Homogeneity brings simplicity because everything comes from a single source and is expected to interoperate together properly. It's a singular offering, though organizations are typically locked into the vendor they select.
In spite of the benefits or homogeneity, heterogeneous data centers evolved to dominate the IT landscape because every enterprise has computing problems that must be solved, but the answer is rarely the same for every company or every problem. The promise of heterogeneity frees an enterprise to mix and match equipment, software and services. This lets the business choose between low-cost product options and optimized ones -- and everything in between -- all while keeping the data center largely free of vendor lock-in.
But heterogeneity has a price. Constructing an effective heterogeneous data center infrastructure requires time and effort. Hardware and software must be individually procured, integrated, configured, optimized -- if possible -- and then managed through tools that are often unique to a vendor's own products. Thus, managing a diverse heterogeneous infrastructure usually requires expertise in multiple tools that IT staff must master and maintain. This causes additional time and integration challenges when the infrastructure needs to be changed, repaired or scaled up. Traditional heterogeneous IT simply isn't all that agile.
Today, business changes at an astonishingly fast pace. IT must respond to the demands of business almost immediately, provisioning new resources for emerging workloads on demand and adding new resources often just in time to keep enterprise applications running and secure. Yet, IT must also eliminate systems management errors and oversights that can leave critical systems vulnerable. And all of this must be accomplished with ever-shrinking IT budgets and staff. Hyperconverged infrastructure is all about deployment speed and agility.
HCI draws on the same benefits that made homogeneous data center environments popular: single-vendor platforms that ensured compatibility, interoperability and consistent management, while providing one vendor to interrogate when something went wrong. But HCI goes deeper to deliver compute, storage and network resources that are organized using software-defined and virtualization-based technologies. The resources are tightly integrated and pre-optimized, and the hardware and software are packaged into convenient appliances -- or nodes -- which can be deployed singularly to start and then quickly and easily scaled out as resource demands increase.
In short, HCI products are essentially envisioned as data centers in a box. If a business needs more resources, just add more modules to the HCI box. If one HCI box is not enough for the data center, just add more boxes. But the appeal of HCI extends beyond the data center. The compact, highly integrated offerings are easily installed and can be managed remotely, and HCI technology has become a staple of remote office/branch office (ROBO) and edge computing deployments.
As an example, consider a typical big data installation where petabytes of data arrived from an army of IoT devices. Rather than rely on an expensive, high-bandwidth network to send raw data back to a data center for processing, the data can be collected and stored locally at the edge -- where the data originates -- and an HCI deployment can readily be installed at the edge to remotely process and analyze the raw data, eliminating network traffic congestion by sending only the resulting analysis to the main data center.
As another example, consider an organization with a private or hybrid cloud initiative. A traditional effort would involve adding and provisioning infrastructure required to support a private cloud stack. An HCI deployment provides a convenient, all-inclusive "data center in a box" that can be configured and deployed as a private cloud, subsequently connected to a public cloud to build a hybrid cloud infrastructure for the business.
Why more companies are adopting HCI
In 2020, the hyperconverged infrastructure market was generating about $2 billion in sales per quarter. By 2022, the global HCI market was valued at $4.8 billion, and is expected to grow to $19.7 billion by 2028. This tremendous investment has taken HCI from a niche or SMB platform to a viable enterprise alternative. Although HCI might not be ideal for all workloads, HCI is able to tackle a greater range of applications and use cases than ever before.
HCI started as a point platform, a means of simplifying and accelerating modest IT deployments in ROBO as well as a limited number of enterprise-class environments, such as virtualized desktop infrastructure (VDI). Early on, large businesses used HCI to support mission-specific goals separate from the main production environment, which could be left alone to continue doing the heavy lifting.
Today, HCI remains a powerful point solution for a wide array of IT project initiatives. HCI offerings benefit from the radical improvements that have taken place in processors, memory and storage devices, as well as dramatic advances in software-defined technologies that redefine how businesses perceive and handle resources and workloads. Examples include the following:
- HCI support for container clusters. Vendors routinely offer HCI configurations optimized for popular container software, such as Kubernetes.
- Support for machine learning and deep learning algorithms. The ability to support a huge volume of scalable containers makes HCI a natural fit for machine learning (ML) and artificial intelligence (AI) workloads, which demand enormous numbers of compute instances or nodes.
- The emergence of streaming data analytics. Streaming analytics is an expression of big data, allowing an HCI system to ingest, process and report on data and metrics collected from a wide array of sources in real time. Such analytics can be used to yield valuable business insights and predict impending problems or faults.
Hyperconverged infrastructure has had a profound effect on edge computing. Today's unparalleled proliferation of IoT devices, sensors, remote sites and mobile accessibility is demanding that organizations reconsider the gathering, storing and processing of enormous data volumes. In most cases, this requires the business to move data processing and analysis out of the central data center and relocate those resources closer to the source of the data: the edge. The ease and versatility provided by HCI offerings makes remote deployment and management far easier than traditional heterogeneous IT infrastructures.
Finally, the speed and flexibility in HCI has made it well suited to rapid deployment, and even rapid repurposing. The realities of the COVID-19 pandemic have forced a vast number of users to suddenly work from home. This has made organizations have to suddenly deploy additional resources and infrastructure to support the business computing needs of users now working remotely. HCI systems have played a notable role in such rapid infrastructure adjustments.
Hyperconverged infrastructure vs. converged infrastructure
Today's hyperconverged infrastructure technologies didn't spring into being overnight. The HCI products available today are the result of decades of data center -- and use case -- evolution. To appreciate the journey, it's important to start with traditional data center approaches where compute, storage and network equipment were all selected, deployed and usually managed individually. The approach was tried and true, but it required careful integration to ensure that all of the gear would interoperate and perform adequately. Optimization, if possible at all, was often limited.
As the pace of business accelerated, organizations recognized the deployment and performance benefits of integration and optimization. It took a long time to optimize and validate a heterogeneous IT hardware and software infrastructure stack. If it were possible to skip the challenges of integrating, configuring and optimizing new gear and software, deployments could be accomplished faster and with fewer problems.
This gave rise to the notion of convergence, enabling vendors to create predefined sets of server, storage and network gear -- as well as software tools -- that had been prepackaged and pre-integrated, and were already validated to function well together. Although CI was basically packaged gear from several different vendors, the time-consuming integration and optimization work had already been accomplished. In most cases, a software layer was also included, which could manage the converged infrastructure products collectively, essentially providing a single pane of glass for the given CI package.
Eventually, vendors realized that convergence could provide even greater levels of integration and performance by foregoing multiple vendors' products in favor of a single-vendor approach that combined compute, storage, network and software components into a single packaged product. The concept was dubbed hyperconvergence and led to the rise of hyperconverged infrastructure.
HCI products are often denoted by a modular architecture, enabling compute, storage and network components to be built as modules that are installed into a specialized rack. The physical blade form factor proved extremely popular for HCI modules and racks, enabling rapid installation and hot swap capabilities for modules. More compute, storage and network blades could be added to the blade rack. When the rack was filled, a new rack could be installed to hold more modules -- further scaling up the deployment. From a software perspective, the HCI environment is fully virtualized and includes unified management tools to configure, pool, provision and troubleshoot HCI resources.
HCI 1.0 vs. HCI 2.0
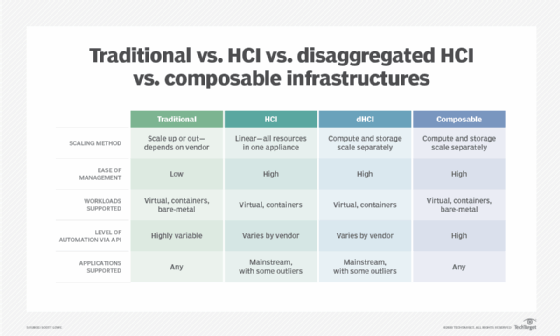
Hyperconverged infrastructure continues to evolve, expressing new features and capabilities while working to overcome perceived limitations and expand potential use cases. Today, there is no commonly accepted terminology to define the evolution of HCI, but the technology is colloquially termed HCI 1.0 and HCI 2.0. The principal difference in these designations is the use of disaggregation.
The original premise of HCI was to provide tightly integrated and optimized sets of virtualized CPU, memory, storage and network connectivity in prepackaged nodes. When more resources are needed, it's a simple matter to just add more nodes. Unified management software discovered, pooled, configured, provisioned and managed all the virtualized resources. The point here was that hyperconverged infrastructure relied on the use of aggregation -- putting everything in the same box -- which could be deployed easily and quickly. It's this underlying use of aggregation that made HCI 1.0 products so appealing for rapid deployment in ROBO and edge use cases.
The major complaint about HCI 1.0 products is the workload resource use and the potential for resource waste. A typical HCI product provides a finite and fixed amount of CPU, memory and storage. The proportion of those resources generally reflects more traditional, balanced workloads. But workloads that place uneven or disproportionate demands on resources can ultimately exhaust some resources quickly -- forcing the business to add more costly nodes to cover resource shortages yet leave the remaining resources underutilized.
Disaggregation is increasingly seen as a potential answer to the problem of HCI resource waste. The introduction of disaggregated hyperconverged infrastructure -- dHCI or HCI 2.0 -- essentially separates compute resources from storage and storage area networks (SANs). HCI 2.0 puts CPU and memory in one device and storage in another device, and both devices can be added separately as needed. This approach helps businesses target the HCI investment in order to support less-traditional workloads that might pose more specific resource demands. Nimble Storage dHCI, NetApp HCI and Datrium DVX are examples of HCI 2.0.
But the evolution of HCI has not stopped with disaggregation, and the entire IT industry is starting to embrace the notion of composable infrastructure. In theory, a composable infrastructure separates all resources into independently scalable and collectively managed components, which can be added as needed and interconnected with a specialized network fabric that supports fast, low-latency communication between components. At the same time, unified management software continues to discover, pool, configure -- or tier -- provision and manage all of the resources available.
Today, composable infrastructure is still far from such an ideal scenario, but vendors are starting to deliver HCI devices with greater versatility in hardware selection and deployment -- such as allowing other nonvendor storage to be added. The key to success in any composable infrastructure is management software that must focus on resource discovery, pooling, tiering -- organizing resources based on their relative level of performance -- and almost total dependence on software-defined behaviors to provision resources.
Hyperconverged infrastructure and the cloud
It's easy to confuse HCI and cloud technology. Both rely on virtualization and a mature software management layer that can define, organize, provision and manage a proliferation of hardware resources and services that enterprise workloads can operate within. Although HCI and cloud can interoperate well together, they aren't the same thing, and there are subtle but important differences to consider.
HCI is fundamentally a centralized, software-driven approach to deploying and using a data center infrastructure. The underlying hardware is clearly defined, and the amount of hardware resources is finite. Virtualization abstracts the resources, while software organizes and defines the ways resources are provisioned to workloads.
A cloud is intended to provide computing as a utility, shrouding vast amounts of virtualized resources that users can provision and release as desired through software tools. The cloud not only provides a vast reservoir of resources but also a staggering array of predefined services -- such as load balancers, databases and monitoring tools -- that users can choose to implement.
Essentially, the difference between HCI and cloud is the difference between hardware and software. HCI is merely one implementation of hardware that can be deployed in a data center. A cloud is really the software and constituent services -- the cloud stack -- built to run atop the available hardware. Thus, an HCI deployment can be used to support a cloud, typically a private cloud or a private cloud integrated as part of a hybrid cloud, aiding in digital transformation. Conversely, a cloud software stack, such as OpenStack, will run on an HCI deployment within the data center.
For example, Azure Stack HCI is a version of Microsoft Azure public cloud stack designed to run on local HCI hardware. Similarly, Dell's VMware Cloud Foundation on VxRail is an example of an HCI offering that includes a suite of software that can be used to operate the HCI platform as a private cloud -- and streamline the private cloud into public cloud environments, such as VMware on AWS.
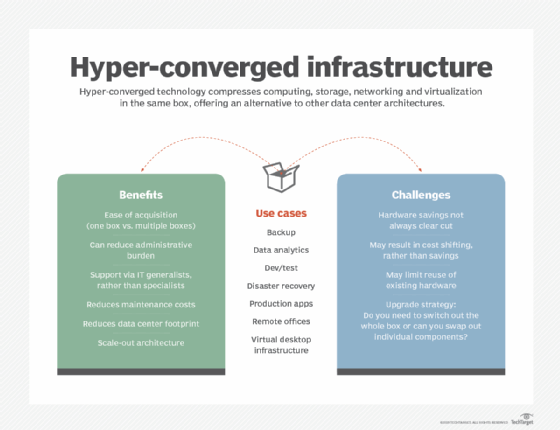
What are the benefits and use cases of hyperconverged infrastructure?
Hyperconverged infrastructure might not be appropriate for every IT project or deployment. Organizations must take the time to evaluate the technology, perform proof-of-concept testing and carefully evaluate the tradeoffs involved before committing to HCI. However, HCI brings several noteworthy benefits to the enterprise, including the following:
- Simplicity in hardware. The main advantage of HCI is simplicity, and the notion of simplicity expresses itself in several different ways. For example, the modular nature of an HCI offering simplifies deployment. Installation time is vastly reduced, and the time needed to configure the installed system and make resources available to workloads is also potentially shorter than traditional hardware deployments. When additional resources are needed, it's a simple matter to install another HCI node, and HCI vendors often offer several different node types -- such as nodes with additional storage or additional compute -- to suit different workload needs. Typical integration problems and optimization challenges are significantly reduced because the HCI system is designed from the ground up for interoperability and optimization.
- Superior systems management. Simplicity also expresses itself in terms of faster and more efficient HCI management. The use of a unified management platform ensures that all HCI resources are discovered, pooled, configured properly -- following the organization's preferred guidelines for security and business process -- and provisioned efficiently, with all resources visible and monitored. HCI systems lend well to automation in provisioning and maintenance, which is a reason that HCI has become popular with private cloud, VDI and other types of IT projects that benefit from automation. This can be more effective than heterogeneous environments, which might demand multiple management tools and can inadvertently overlook resources if not properly discovered.
- Better support. Ultimately, HCI deployment and time to production is easier and faster than traditional heterogeneous deployments, enabling HCI to be deployed and supported by smaller businesses with a smaller IT staff and fewer technical skills. Such simplicity also translates into ongoing service and support. Because HCI comes from a single vendor, support is also part of the package, ensuring that one call to technical support should yield tangible solutions to pressing problems; there is no other vendor to blame. This also helps smaller and less skilled IT staff. Taken together, the simplicity and ease promised by HCI can lower the costs of deploying and operating an HCI.
- Better optimizations and performance. Bringing compute, storage and network assets together in a well-integrated platform can lead to better optimizations and superior performance for some workload types when compared to traditional heterogeneous infrastructures. This can be especially true for workloads that depend on agility and high scalability.
- Better cost management. IT can be a costly resource for any modern enterprise, and budgets for IT gear and software tools are stretched thin. HCI is not necessarily cheaper than traditional heterogeneous IT, but HCI can help to ensure that the IT spend solves intended problems -- or meets intended goals -- while being easier to install and maintain. Disaggregated and composable technologies help ensure that additional IT spend provides the resources needed without wasting spend on idle or unneeded assets.
HCI can typically support a wide range of enterprise computing use cases, including general-purpose workloads. But some important HCI use cases include the following:
- Centralized services. The storage and compute potential of HCI systems can be an excellent match for highly virtualized and centralized services such as remote desktops including VDI and desktop as a service.
- Cloud initiatives. Rather than reallocating traditional heterogeneous IT infrastructure for a private cloud, HCI systems can be deployed to serve as a separate packaged cloud-in-a box, which can be accessed as a private cloud or integrated with a public cloud to form a hybrid cloud.
- Data protection. HCI systems routinely include features that tie directly to data protection, such as backups, snapshots, DR and data security.
- Databases. Databases demand high performance and high reliability because many other enterprise workloads access and depend on databases for everyday operation.
- Edge computing. HCI is often an ideal choice for edge computing requirements where high integration, scalability and performance is needed to collect, store and process huge amounts of data with little human intervention such as IoT environments.
- File storage. File storage -- or file servers -- are one common general-purpose workload type that HCI can be well suited for because of its data protection capabilities and high-performance potential. HCI can also provide extremely high storage capacities and support SANs.
- Logging and analytics. Log analysis and analytical tasks, such as data mining, demand fast compute performance and must support high data velocity that HCI systems are noted for.
- Test and development. HCI provides well-managed infrastructure resources, which can be ideal for software development and testing tasks, enabling developers to allocate and free resources as required.
What are the drawbacks of HCI?
In spite of the many noteworthy benefits, HCI also poses several potential drawbacks that deserve careful consideration. Common HCI disadvantages or limitations can include the following:
- Vendor lock-in. Scalability comes at the cost of vendor lock-in. It's a simple matter to add another node, but only if the new node comes from the same vendor. There are no open standards for physical or logical interoperability between nodes of different HCI systems or vendors. Conventional HCI -- HCI 1.0 -- systems also aggregate CPU, memory and storage into the same node, so buying more of one resource almost always means buying more of all resources -- even if other resources aren't currently needed -- which can be a waste of resources and capital investment. The push toward disaggregation, such as HCI 2.0 or dHCI, promises to help ease such waste.
- High power density and cooling demands. HCI can pose problems with power density. Packing huge amounts of hardware into such relatively tight physical spaces can wreak havoc with power distribution systems and demand point cooling in data centers that have long eased power and cooling density concerns. This means HCI installation is simple, but only if power and cooling demands are met.
- Limited scalability and redundancy. The scale of HCI is still small. Although this isn't an issue for many workloads, larger deployments that involve many compute servers and tens of terabytes of storage might be better served with separate compute and storage subsystems. This traditional approach more closely resembles disaggregation and lets demanding subsystems be scaled and optimized separately. Large volumes of server or storage purchases can also benefit from economies of scale that HCI products can't provide.
- Not all features are default. Some high-end features of HCI, such as high availability, might not be available without additional purchases. For example, an HCI node isn't really redundant unless there's at least a second HCI node running parallel workloads alongside the first one. This represents additional investment that the organization might not be able to make, at least initially. Similarly, support for cloud and public cloud integrations are not guaranteed and will require careful testing and proof-of-concept testing.
- Cost. One of the recurring drawback themes is HCI costs. HCI products are vendor-centric and typically carry a premium price tag because there is no unified interoperability between vendor offerings. Aggregated nodes can impose unwanted capital expenses for resources that might not all be needed. Software licensing and maintenance contract costs can drive up recurring HCI costs. And costs might also fluctuate with node types. For example, HCI vendors typically provide several different node options to offer various combinations of CPU, memory, storage and network connectivity to accommodate varied workload needs. Selecting nodes with high-end CPUs, non-volatile storage, 10 Gigabit Ethernet and other options can drive up the price tag for an HCI deployment.
HCI management and implementation
Although HCI brings an array of powerful benefits to the enterprise, there are also numerous management and implementation considerations that must be carefully evaluated and understood before an HCI investment is ever made. These include the following:
Resiliency. One critical issue is resiliency. HCI simplifies deployments and operation, but the simplicity that users see hides tremendous complexity. Errors, faults and failures can all conspire to threaten application performance and critical business data. And while HCI offerings can support resiliency, the feature is never automatic, and it can require detailed understandings of the HCI system's inner workings, such as write acknowledgement, RAID levels or other storage techniques used for resiliency.

To understand the ways that an HCI offering actually handles data resiliency, IT leaders must evaluate the offering and consider how the system handles node or hardware module failures, the default operations of data resiliency operations, the additional costs of HCI resilience options, the workload performance effect of using resiliency options and the overhead resource capacity that is used to provide resiliency.
Management. When it comes to HCI systems management, users can often benefit from third-party management tools, such as DataOn Must for Windows Admin Center. By exposing APIs, third-party tools and services can connect to HCI to provide a wider array of services or integrations.
HCI deployments and management also benefit from a clear use case, so it's important to understand any specific or tailored roles that an HCI system plays in the environment and manage those roles accordingly. For example, an HCI deployment intended for backup and DR is likely to be managed and supported differently -- and rely on different management features -- than an HCI deployment used for everyday production workloads.
Take advantage of any automated policy management and/or enforcement that the HCI system provides. Emerging software-defined tools, such as Nutanix Flow Network Security, can enable network and policy management that helps to speed provisioning while enforcing best practices for the business, such as configuration settings adjustment and application security implementation. Such capabilities are often adept at reporting and alerting variations from policy, helping businesses maintain careful control over resource use and configurations.
Finally, use care in choosing management tools. The native tools that accompany HCI systems are usually proprietary and typically might not interoperate easily -- if at all -- with other heterogeneous servers, storage and network elements across the data center. Organizations that must monitor and manage broader heterogeneous environments without the silos that accompany multiple management tools might benefit from adopting comprehensive third-party tools, such as Zenoss, Uila, EG Innovations EG Enterprise and ManageEngine OpManager. Third-party tools must be tested and vetted thoroughly before being implemented in mixed environments to ensure that all elements are visible and reported properly.
Major HCI vendors and products
There are numerous vendors and products across the HCI space. Principal HCI vendors and products include the following:
- Cisco HyperFlex systems.
- HPE SimpliVity family of systems.
- Huawei FusionCube system family.
- Huayun (Maxta) HCI.
- IBM Storage Fusion HCI.
- Microsoft Azure Stack HCI.
- Nutanix AHV and Nutanix Cloud Platform.
- Sangfor HCI.
- Scale Computing SC/HyperCore platform.
- SmartX HCI.
- VMware vSphere, vSAN and other virtualization software platforms.
HCI offerings typically fall into software-based or hardware-based deployments.
Software-based deployments focus on the "software-defined" capabilities that virtualization and HCI promise, enabling vendors to build more ubiquitous HCI software platforms that can interoperate with a much broader range of existing systems hardware within the enterprise -- often minimizing the required investment and reducing vendor lock-in.
As an example, Nutanix follows a software-based approach to HCI. The goal for Nutanix AHV is to provide a software layer that can provide the features and functionality needed for HCI yet support a broad mix of software and hardware. Nutanix does offer its own purpose-built NX hyperconverged appliances, but appliances made by Cisco, HPE, Hitachi, NEC, Intel and other vendors can also use Nutanix software. Thus, Nutanix is broadly seen as a general-purpose HCI platform. Other vendors with software-based HCI offerings include VMware and Microsoft Azure Stack HCI.
Hardware-based deployments underscore the highly integrated and carefully managed nature of HCI as a concept. Vendors will generally provide servers, storage and network gear that are already known to interoperate efficiently using a common management tool. Virtualization and management software are included atop the hardware stack.
For example, HPE provides the family of SimpliVity HCI platforms as a more familiar hardware-based approach to HCI. SimpliVity promises more of a balance between hardware and software by using a software HCI foundation running on HPE DL380 Gen10 servers as a use case-based hardware platform. For example, the HPE SimpliVity 380 Gen10 Plus is recommended for best general-purpose performance, while the Gen10 G variant is recommended for multi-GPU image processing and VDI. The product family touts enterprise-class performance, data protection and resiliency, along with a high level of automation and analytics driven by HPE management and analytics. Other vendors with hardware-based HCI offerings include Cisco and Scale Computing.
HCI future trends
HCI technology has not remained idle as vendors and users alike seek new -- often niche -- use cases that push beyond traditional VDI, edge and private or hybrid cloud foundation use cases. HCI is making strides in data center automation and analytics where software layers can easily access tightly integrated hardware to monitor capacity, assist with upgrades, handle provisioning and warn of potential system problems.
Hardware choices are also advancing, with some software-based HCI able to accommodate a diverse array of servers and storage, while hardware-centric offerings move to support more demanding use cases -- such as adding NVMe support for SAP HANA. Similarly, HCI seems to be gaining traction as a data protection, backup or DR platform for enterprise uses, sometimes in conjunction with cloud services. Finally, the role of cloud providers in HCI is starting to gain traction, with offerings such as AWS Outposts providing both hardware and software for enterprise uses.
Ultimately, HCI is likely to see continued adoption and growth in important technology areas over the next several years including private/hybrid cloud computing projects, analytics and ML/AI tasks, expanding edge computing environments and greenfield sites where deployment speed and management simplicity are primary design considerations.
Editor's note: The HCI vendors and products list was assembled from various industry research sources and presented in unranked, alphabetical order.
Stephen J. Bigelow, senior technology editor at TechTarget, has more than 20 years of technical writing experience in the PC and technology industry.







